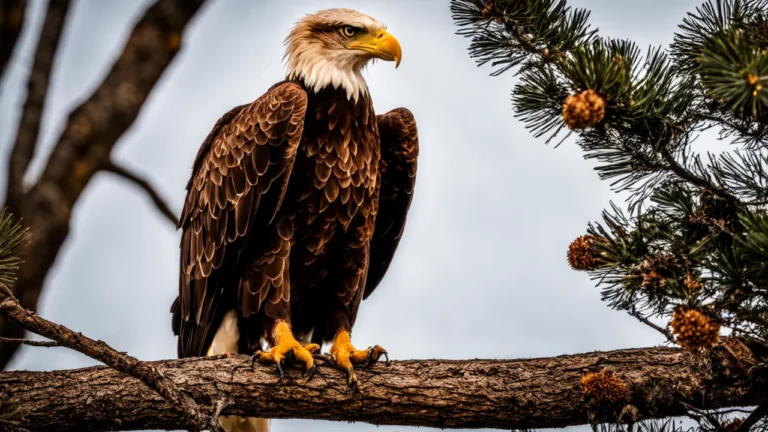
In the world of birds, eagles are among the most fearsome hunters because to their sharp talons, lethal accuracy, and acute vision. Does it, however, mean that they are the top predators in the food chain? This is a simple response in case you’re pressed for time: Yes, in most of the environments in which they reside, eagles are regarded as apex predators.
We’ll explore eagles’ predatory tendencies and their position as top predators in this extensive tutorial. Their hunting techniques, the prey they pursue, and their interactions with other apex predators will all be covered.
You’ll comprehend why eagles occupy the highest position in several food webs at the conclusion.
Eagles Possess Apex Predator Qualities
With a variety of characteristics that place them at the top of their respective ecosystems’ food chains, eagles are renowned for their exceptional hunting skills. Over millions of years, these magnificent birds have developed into very skilled hunters with the weapons needed to catch their prey.
Strong talons and beaks for hunting prey
Eagles are apex predators, and one of their main distinguishing features is the strength of their talons and beaks. Their beaks are curved and pointed, making them capable of tearing through flesh to effectively catch and eat their meal.
They also have a good grasp on their prey because to their powerful, muscular talons, which guarantees a safe hold during the hunt.
Superior eyesight for identifying distant prey
Because of their exceptional vision, eagles can detect prey at a considerable distance. Eagles can readily identify minute motions or possible prey items from a great height in the sky because to eyes that are up to eight times more powerful than those of humans.
Their remarkable sense of vision offers them a major edge in spotting their next food.
Swiftness and dexterity in the air to pursue prey
Eagles are the fastest and most agile animals when it comes to hunting. These birds can fly through the air at astounding rates, reaching up to 100 miles per hour during a dive, because to their 7-foot wingspans.
They are fearsome hunters in the skies because of their rapid and accurate movements, which let them to swiftly close in on their victim.
Eagles Chase a Broad Range of Prey
Eagles have a varied diet that includes a broad range of food, and they are renowned for their exceptional hunting abilities. They are opportunistic hunters that have evolved to live well in a variety of settings, including marshes, woods, and grasslands.
From amphibians and fish to mammals and birds
The capacity of eagles to capture fish is well-known, and for many eagle species, it is their main source of sustenance. They can dive into the water to grab fish or seize them from the surface because to their strong claws and pointed beaks. Eagles do not, however, just hunt fish.
They also hunt other water animals like crabs and frogs.
Eagles hunt not just watery prey but other birds and animals with expertise. They are often seen flying high in the sky and scouring the terrain for possible food sources. When they see a target, they will swiftly and precisely swoop down to capture their meal.
Small birds, mammals like rabbits or squirrels, and sometimes even bigger species like foxes or deer may be included in this.
Target young, ill, or wounded animals that are at risk.
As skilled predators, eagles are known to pick out weaker members of their prey. They can identify damaged or weak animals as well as young or unskilled ones. They may increase their hunting success by using this tactic since these people are often simpler to capture and tame.
Eagles can see well at long distances, because to their acute sense of vision. They have the ability to sense motion and even the slightest reflection of sunlight off a fish’s scales. Eagles are powerful predators due to their hunting skills and sharp eyesight.
Assist in managing the numbers of tiny prey species
Because they manage the numbers of minor prey species, eagles are crucial to the preservation of ecological equilibrium. For instance, eagles assist in controlling the population of rodents and small animals in places where they are prevalent.
They keep overcrowding and its possible detrimental effects on the ecology at bay by feeding on these smaller creatures.
Eagles’ presence may potentially have a domino effect on other species further up the food chain. Due to their hunting activities, scavengers that feed on the remnants of the eagle’s prey, such vultures or carrion-eating mammals, may have more possibilities to feed themselves.
Eagles Have Few Natural Predators
Eagles are magnificent predators with amazing vision and hunting prowess. They usually occupy the top spot in their respective environments’ food chains as apex predators. Eagles have few natural predators because of their size, power, and aggressive nature, even if they may encounter certain hazards in their area.
Sometimes eaten by bigger animals such as huge cats or wolves
Even though they are fierce hunters, eagles may sometimes become prey for bigger predators. Eagles may fall victim on occasion in areas where wolves or large cats are common, such the isolated wilderness areas of North America or the African savannas.
These bigger predators may take advantage of the weakness of young or wounded eagles by targeting them.
Some dangers posed by snakes or rival raptors
Aside from bigger animals, snakes and other rival raptors pose a hazard to eagles. A few snake species, such as the formidable python or anaconda, have been known to ambush and subdue eagles.
Furthermore, there’s a chance that owls and falcons, among other raptors, could clash over territory or fight for the same food supplies, which might result in fights and even predation.
But have less daily pressure from predators
Despite these sporadic dangers, eagles often experience little consistent pressure from predators. The majority of prospective predators find them to be difficult foes due to their enormous size, keen talons, and strong beaks.
Eagles are often seen as apex predators that manage the numbers of lesser prey species within their own habitats. Because they are not often preyed upon, eagles are able to concentrate on their hunting skills and continue to hold their position as top predators.
Superiority Against Scavengers
Eagles have a distinct edge over scavengers when it comes to dominance. The remarkable hunting prowess of these magnificent birds of prey is well-known, as is their capacity to seize food supplies before other scavengers do.
Obtain carrion ahead of vultures and other scavengers.
Getting first dibs on carrion, or dead animals, is one way eagles show their authority. Their vision is excellent, and they can detect corpses at a considerable distance. They have an advantage over vultures and other scavengers that use their sense of smell to find food because of this.
Before the scavengers even notice there is carrion, eagles may soar above and get it for themselves.
A research by the Cornell Lab of Ornithology found that vultures took far longer to find a corpse than eagles, who arrived at it in a matter of minutes. Eagles have a major advantage over other scavengers in the scavenging hierarchy because of their ability to locate and collect food fast.
Will pilfer food from other predators and smaller raptors.
Eagles are adept at snatching carrion, but they have also been seen robbing smaller raptors and other predators of their prey. Because of a habit known as kleptoparasitism, eagles are able to profit from the hunting endeavors of other animals and birds.
For instance, eagles have been seen mid-air taking fish from ospreys’ talons. They will also intimidate and force other raptors, such falcons or hawks, to abandon their prey so they may take food from them.
This self-serving conduct highlights the eagles’ superiority over other predators and scavengers.
Even though they are apex predators in and of themselves, eagles clearly have the upper hand against scavengers. Their excellent hunting abilities and flexibility are shown by their propensity to steal food from smaller raptors and predators, as well as their ability to obtain food supplies before vultures and other scavengers.
It makes sense that eagles are often thought of as the monarchs of the heavens.
Final Thoughts
Eagles in the majority of ecosystems are unquestionably apex predators. Eagles are at the top of the food chain due to their exceptional hunting skills, varied diet, absence of natural predators, and competitive superiority over scavengers.
As apex predators, eagles contribute to the balance of the environment by carrying out this duty.




![17 Beautiful Blackbirds with Orange Beaks [Pictures + IDs]](https://birdsology.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/27-600x400.jpg)
One thought on “Are Eagles Apex Predators?”