Utah is for its stunning landscapes, from towering mountains to expansive deserts. It’s also home to a diverse range of bird species, including the striking blue bird. These birds are known for their vibrant blue plumage, unique songs, and interesting behaviors, making them a favorite among birdwatchers and nature enthusiasts. In this blog post, we’ll explore the world of blue birds in Utah, from their preferred habitats and migratory patterns to the best locations for observing them in the wild. Whether you’re an experienced birder or simply interested in learning more about the natural world, join us as we discover the fascinating world of blue birds in Utah and gain a deeper appreciation for the state’s rich ecological diversity.
Types of Blue Birds in Utah:
- Barn Swallow
- Belted Kingfisher
- Blue Grosbeak
- Blue-Gray Gnatcatcher
- Common Grackle
- Lazuli Bunting
- Mountain Bluebird
- Pinyon Jay
- Purple Martin
- Red-Breasted Nuthatch
- Rock Pigeon
- Steller’s Jay
- Tree Swallow
- Western Bluebird
- White-Breasted Nuthatch
Barn Swallow

Image Source
- Scientific name: Hirundo rustica
- Lifespan: 4 years
- Size: 5.5 and 7 inches
- Native to: Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas
The barn swallow is a small bird with a distinctive appearance. It measures about 7 inches in length and has shiny steel-blue feathers on its back. Its forehead and throat are chestnut in color, while its underparts are a rusty-orange shade. One of its noticeable features is its long forked tail, which has a white base. It’s worth noting that the female barn swallow has lighter coloring and a shorter tail compared to the male.
When it comes to their diet, barn swallows primarily feed on insects, with a preference for beetles, wasps, and flies. They have a unique way of getting a drink by skimming the surface of the water, but they are not typically seen visiting bird feeders.
These birds are commonly found in open fields and pastures, where they build their nests. Barn swallows prefer manmade structures such as barns for nesting. They construct their nests using mud. During the breeding season, they produce two broods, each containing 4-5 white eggs with brown markings. The incubation period for these eggs ranges from 13 to 17 days.
Barn swallows are migratory birds. In the spring, they migrate north to the United States and Canada for breeding and raising their young. When autumn arrives, they head south to the southern states of Mexico. However, some barn swallows remain in central Mexico throughout the year, maintaining a year-round range there.
Belted Kingfisher

Image Source
- Scientific name: Ardea alba
- Lifespan: 15 years
- Size: 3 feet
- Native to: Asia, Africa, the Americas, and southern Europe
The belted kingfisher is a relatively large bird, measuring about 13 inches in length. It has a distinctive appearance with a large head, a long bill, and a stout body. The bird is predominantly blue-gray in color with a white ring around its neck and a white chest. However, the female belted kingfisher is similar in appearance to the male but features an additional chestnut band on her chest.
When it comes to their diet, belted kingfishers primarily feed on fish. They are not commonly seen at bird feeders but are often attracted to areas with streams or ponds.
These birds are typically found in habitats near bodies of water, including streams, rivers, ponds, lakes, and calm marine waters, especially those with clear water and minimal vegetation.
For nesting, belted kingfishers dig burrows along the water’s edge. They usually have 1-2 broods per season, each containing 5-8 large, glossy white eggs that are about 1.5 inches long. The incubation period for these eggs lasts for approximately 22-24 days.
Belted kingfishers are known for their migratory behavior, although not all of them migrate. In the spring, migratory individuals head north to places like Montana, North Dakota, northern Minnesota, Canada, and Alaska for breeding and raising their young. When fall arrives, these migratory birds head back south, sometimes as far as Arizona, New Mexico, southern California, and Mexico.
While many belted kingfishers migrate, some choose to stay in their year-round range, which includes all U.S. states except North Dakota and Arizona, as well as the Pacific coast of Canada’s British Columbia. During the winter, some remain in their year-round range, while others continue their migration south to escape the cold temperatures.
Blue-black Grosbeak

- Scientific name: Cyanoloxia cyanoides
- Lifespan: 6-7 years
- Size: 5 to 6-inch
- Native to: Middle America and northwestern South America
Blue grosbeaks are medium-sized birds, approximately 8 inches in length. They are quite eye-catching with their vibrant, large, bright blue bodies and silver bills. You can easily spot chestnut wingbars on them. In contrast, the female blue grosbeak has a primary color that resembles light cinnamon, with wings that are darker in color.
When it comes to their diet, blue grosbeaks enjoy a menu that includes insects, seeds, and grains. If you want to attract them to your yard, offering grain and birdseed can be enticing.
These birds tend to make their homes in areas with thick shrubbery and tall trees. For nesting, they create small cup-shaped nests using twigs and various organic materials, placing them in low-lying trees, shrubs, or bushes. They typically have 1-2 broods per breeding season, with each brood containing 3-5 eggs. The eggs are pale blue to white with occasional brown spots and are relatively small, measuring about 0.8 inches by 0.7 inches. The incubation period for these eggs lasts for approximately 12-13 days.
Blue grosbeaks are migratory birds. During the spring, they embark on a journey north to the United States to breed and raise their young. When fall arrives, they head back south for the winter, with many of them finding refuge in Mexico and the Caribbean islands. However, there is a small group of blue grosbeaks that call a specific area in Mexico their year-round home, and they do not typically migrate like their counterparts. In their year-round range, blue grosbeaks can be found in parts of Mexico, while their breeding range extends across the southern half of the United States, including North Dakota, South Dakota, and Kansas.
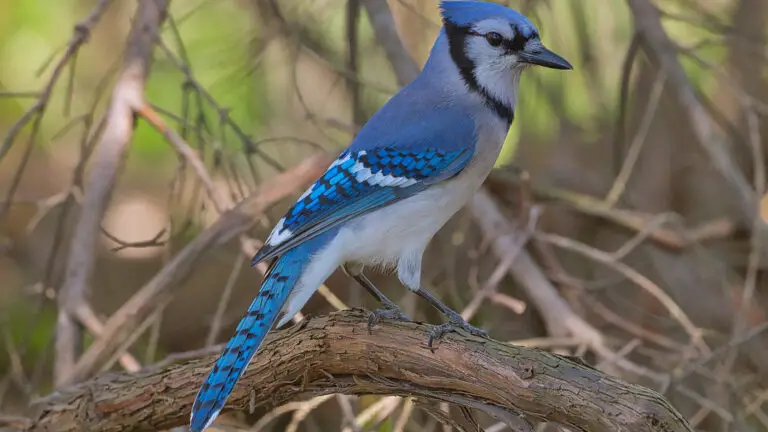
Blue Jay

Image Source
- Scientific name: Cyanocitta cristata
- Lifespan: about 7 years
- Size: 9 and 12 inches
- Native to: North America
The blue jay is a large bird, measuring about 12 inches in length. It has a medium blue and white body with distinctive features like a blue crest on its head, which it can flatten at will. The bird also sports a gray belly and a white face. Its wings are a combination of white and blue with noticeable black spots. Interestingly, both male and female blue jays share the same appearance.
When it comes to their diet, blue jays are omnivorous, which means they eat a variety of foods. They enjoy insects, fruits, seeds, nuts, and they are not averse to consuming other birds’ eggs and nestlings.
For those interested in attracting blue jays to their yards, offering whole peanuts, sunflower seeds, and cracked corn can be enticing.
Blue jays are quite adaptable when it comes to their habitat. They are commonly found in forested areas with mixed types of trees, but they are also a frequent sight in suburban and urban environments.
When it comes to nesting, blue jays build substantial nests made from twigs, bark, and mud, typically resting on tree branches at heights ranging from 5 to 50 feet. During the breeding season, they tend to have 1-2 broods, and each brood can contain 2-7 eggs. The eggs of blue jays vary in color from pale blue to a light brown base, often adorned with brown or gray spots. These eggs are relatively small, measuring about 1 inch by just under 1 inch. Both parents share the responsibility of incubating the eggs, which takes about 17-18 days. The young birds, or fledglings, typically leave the nest between 17 to 21 days after hatching.
Blue jays are known for being non-migratory birds. They tend to stay within their year-round range throughout all four seasons, including the breeding season. While they may move around within this range, they do not have a regular pattern of migrating north for breeding and south for the winter, as some other bird species do. However, in rare instances, some blue jays may venture west of their year-round range during the winter months.
Blue-gray Gnatcatcher (Small Bluebirds In Florida)

Image Source
- Scientific name: Polioptila caerulea
- Lifespan: 3-4 years
- Size: 3.9–5.1 in
- Native to: North America
The blue-gray gnatcatcher is a tiny bird, measuring around 4.25 inches in length. These birds have soft blue-gray feathers on their upperparts, distinctive white eye-rings, and white underparts. They are characterized by their long black tails with white undersides. Interestingly, both male and female blue-gray gnatcatchers look the same in terms of their appearance. However, during the breeding season, the male may have narrow black eyebrows that accentuate its features.
When it comes to their diet, blue-gray gnatcatchers primarily feed on insects and spiders, which they catch as they dart through the air.
These birds are not commonly seen visiting bird feeders. They tend to prefer foraging for insects in their natural environment.
Blue-gray gnatcatchers are typically found in deciduous forested areas, where they make their nests and raise their young.
For nesting, they create tidy cup-shaped nests using natural fibers, bark, and spiderwebs. These nests can be situated at heights ranging from 3 to 80 feet in trees or shrubs. During the breeding season, they usually have 1-2 broods, with each brood consisting of 3-5 pale blue eggs with red or brown spots. The eggs are quite small, measuring between 0.5 to 0.6 inches by 0.4 to 0.5 inches. The incubation period lasts for approximately 11-15 days, and the young birds, or fledglings, typically leave the nest at around 10-15 days old.
Blue-gray gnatcatchers exhibit migratory behavior. While some of them stay within their year-round range during spring and summer, most migrate north into the United States to breed and raise their young. In the fall, these migratory individuals head back south, returning to their year-round range or even traveling further south along the Mexican Pacific coast, southern Florida, and the Caribbean islands to spend the winter.
Their year-round range includes the southernmost parts of several U.S. states, such as California, Arizona, New Mexico, Texas, Louisiana, Georgia, Mississippi, Alabama, Florida, South Carolina, North Carolina, and Virginia. Their breeding range encompasses the eastern half of the United States, as well as parts of California, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, Colorado, New Mexico, Texas, Kansas, and Oklahoma. During the winter months, they can be found in regions including southern California, southwest Arizona, along the Pacific coast of Mexico, the southernmost tip of Florida, and various Caribbean islands.
Common Grackle

Image Source
- Scientific name: Quiscalus
- Lifespan: 17 years
- Size: 11-inch
- Native to: North and South America
The common grackle is a relatively large bird, measuring around 12.5 inches in length. These birds are easily identifiable by their iridescent blue-purple and bronze plumage. They have striking yellow eyes and distinctive long, flared tails. While both male and female common grackles share similar features, the female tends to have less vibrant coloring, appears somewhat browner, and possesses a shorter tail.
In terms of their diet, common grackles have diverse preferences, as they feed on insects, grains, seeds, and fruit, and even scavenge for discarded food in the garbage.
When it comes to attracting common grackles to bird feeders, offering sunflower seeds, particularly black-oil sunflower seeds, can be enticing.
These birds are adaptable when it comes to their habitat, and they are commonly found in fields with scattered trees, open woodlands, farmlands, and marshes. It’s not uncommon to spot common grackles in suburban yards as well.
For nesting, common grackles construct bulky cup-shaped nests made of twigs. They typically place these nests at heights ranging from 3 to 20 feet in conifer trees. Their nests usually contain 3-5 eggs, which are incubated for about 12-15 days. The young birds, or fledglings, typically leave the nest at around 12-15 days old.
Common grackles exhibit migratory behavior. While some remain within their year-round range throughout all four seasons, many migrate north in the spring, venturing as far north as Canada’s Northwest Territories to breed and raise their young. Then, when fall arrives, they head back south into their year-round range. A small portion of the population pushes even further southwest into Texas.
Their year-round range includes Nebraska and the U.S. states located south and east of it. Their breeding range extends to regions such as Montana, Idaho, Wyoming, Colorado, New Mexico, North Dakota, South Dakota, Kansas, western Kansas, Minnesota, Wisconsin, Michigan, the New England states, and all Canadian provinces (except for Nunavut and British Columbia). During the winter months, common grackles can be found along the southwest edge of their year-round range in Texas.
Eastern Bluebird

Image Source
- Scientific name: Sialia sialis
- Lifespan: 6 to 10 years
- Size: 6.3–8.3 in
- Native to: Eastern North America and south as far as Nicaragua
Eastern bluebirds are small birds, measuring about 7 inches in length. They are easily recognizable by their vibrant royal blue plumage, along with an orange throat and breast, and a white belly and undertail. While both male and female eastern bluebirds share similar features, the female tends to have more muted colors.
When it comes to their diet, eastern bluebirds have a varied menu. During the spring and summer months, they primarily feed on insects and spiders. However, as the seasons change to fall and winter, their diet shifts towards small fruits.
For those looking to attract eastern bluebirds to their yards, providing suet, sunflower seeds, dried fruit, and jelly can be enticing food options.
Eastern bluebirds are often found in wide-open spaces, including fields and meadows, where they make their homes and raise their young.
In terms of nesting, eastern bluebirds are cavity nesters. The male bluebird takes on the task of selecting the nest site, which could be an old woodpecker hole in a tree or a manmade nestbox. However, it is the female who is responsible for building the nest. Interestingly, she may reuse the same nest for multiple broods. During the breeding season, they tend to have 2-7 broods, each containing 4-5 pale blue (sometimes white) eggs with no blemishes or discoloration. These eggs are relatively small, measuring about 0.9 inches by 0.8 inches. The incubation period for these eggs typically lasts from 11 to 19 days.
While many eastern bluebirds remain within their year-round range throughout the entire year, some exhibit migratory behavior. These migratory bluebirds head north for breeding and raising their young and then travel south during the winter months. They either return to their year-round range or move further west into regions like Colorado, New Mexico, and western Texas.
Their year-round range encompasses the U.S. states located south and east of Nebraska, as well as Mexico and Central America. During the breeding season, they can be found in regions including northwest Nebraska, South Dakota, North Dakota, Minnesota, the northern half of Wisconsin and Michigan, New Hampshire, Maine, and parts of Canadian provinces such as Saskatchewan, Manitoba, Ontario, and Quebec. In the winter, eastern bluebirds can be spotted in areas including eastern Colorado, New Mexico, western Texas, and northeast Mexico.
Indigo Bunting

Image Source
- Scientific name: Passerina cyanea
- Lifespan: 10 years
- Size: 5 inches
- Native to: Southern Canada to northern Florida during the breeding season, and from southern Florida to northern South America during the winter.
Indigo Buntings are commonly found in a variety of habitats. You can spot them in brushy fields, where they often perch on weedy plants, scrub areas, and along the edges of woodlands. They also make themselves at home in clearings within deciduous woods and along the edges of swamps.
When it comes to their diet, savannah sparrows have a diverse menu. They typically feed on small seeds, insects, and fruits. While they are not regular visitors to bird feeders, you may attract them by offering nyjer/thistle and white millet seeds.
Their preferred habitat includes brushy fields, weedy plants, scrubland, and woodland edges, as well as clearings within deciduous woods and swampy areas.
For nesting, Indigo Bunting create cup-shaped nests, which they usually place in shrubs or trees about 3 feet high off the ground. During the breeding season, they tend to have 1-3 broods, with each brood containing 3-4 eggs. These eggs are white with a few brown spots.
Lazuli Bunting

Image Source
- Scientific name: Passerina amoena
- Lifespan: Up to 6 years
- Size: Approximately 13 centimeters (5.1 inches) in length
- Origin: Native to western North America
The Lazuli Bunting is a small bird, measuring about 5-6 inches in length. It’s known for its striking appearance with brilliant blue feathers on its upper body and a soft orange-cinnamon color on its chest. The bird also features a white belly and a patch of white on its shoulder. Its beak is cone-shaped, and it has a slightly flat forehead.
In terms of diet, Lazuli Buntings have a varied menu. They typically feed on insects, fruits, and grasses. While they forage in nature, you can also attract them to your yard by offering white proso millet, sunflower seeds, or nyjer thistle seeds at bird feeders.
These birds are commonly found in open woodlands, brushy hillsides, thickets, and even in backyard settings throughout the western regions of the United States.
When it comes to nesting, Lazuli Buntings create cup-shaped nests constructed from bark, twigs, and leaves. They usually position these nests in shrubs at a height of about 3 feet above the ground. During the breeding season, they typically have 1-2 broods, and each brood consists of 3-4 eggs. The eggs are relatively small, measuring between 0.7 to 0.8 inches in length. They can be pale blue to faint green/blue or even white in color. The incubation period for these eggs lasts for approximately 11-14 days.
Mountain Bluebird

Image Source
- Scientific name: Sialia currucoides
- Lifespan: Up to 6 years
- Size: Approximately 16-20 centimeters (6-8 inches) in length
- Origin: Native to North America
The Mountain Bluebird is a small bird, measuring about 7 inches in length. They are known for their sky-blue coloring, with darker blue wings and tails. Their undersides are lighter in shade, and they have a distinctive white undertail with black wingtips. These birds have straight, thin bills. Females, on the other hand, have a more subdued appearance, with grayish-brown feathers and a touch of soft blue on their wings and tail.
When it comes to their diet, Mountain Bluebirds have a varied menu. They primarily feed on insects, but they also enjoy consuming fruit and seeds.
While they are not commonly seen at bird feeders, Mountain Bluebirds prefer natural foraging. They are more likely to be found in open woodlands, fields, and prairies.
For nesting, Mountain Bluebirds are cavity nesters. They often use old woodpecker holes in trees or manmade nesting boxes for their nests. During the breeding season, they typically have 1-2 broods, with each brood containing 4-8 eggs. The eggs are relatively small, measuring about 1 inch by 0.8 inches. They can be pale blue to bluish-white, with pure white eggs being a rare occurrence. The incubation period for these eggs lasts for approximately 18-21 days.
Northern Parula

Image Source
- Scientific name: Setophaga americana
- Lifespan: 7 year
- Size: 11.4 cm
- Native to: Florida north to the boreal forest of Canada, but skip parts of Iowa, Wisconsin, Michigan, and some states in the Northeast.
The Northern Parula is a small bird, measuring about 4.5 inches in length. They have a distinctive appearance with blue-gray feathers and a yellow throat and back patch. Their overall coloring is bluish-gray, and they sport a yellow-green patch on their back. You can also spot a brown band on their lower neck and two white strips above and below each eye. Female Northern Parulas have similar features but with more muted colors.
When it comes to their diet, Northern Parulas have a diverse menu. They feed on spiders, insects, berries, seeds, and nectar.
While they are not typically seen at bird feeders, Northern Parulas prefer natural foraging. They are often found in forested areas, particularly where water is present, such as near streams and marshes. They also thrive in lowland areas where moss is abundant.
For nesting, Northern Parulas build their nests within mossy vegetation, often at heights of up to 100 feet at the end of a branch. During the breeding season, they typically have 1-2 broods, with each brood containing 2-7 eggs. These eggs are relatively small, measuring about 0.65 inches in length. They are white with red, brown, or purple speckles. The incubation period for these eggs lasts for approximately 12-14 days.
Northern Parulas are migratory birds. In the spring, they migrate north to breed and raise their young. Then, when the fall arrives, they migrate south for the winter.
Their breeding range includes the U.S. states located south and east of Kansas, as well as northern Minnesota, Wisconsin, and Michigan, along with parts of Pennsylvania, New York, New England, and the southern regions of Canadian provinces like Manitoba, Ontario, and Quebec. During the winter months, you can find Northern Parulas in the southern tip of Florida, the Caribbean islands, Mexico, and Central America.
Pinyon Jay

The Pinyon Jay is a bird that measures approximately 10-11 inches in length. These birds have a distinctive appearance with a dusty blue body, a lighter blue belly and throat, a short tail, and no crown on their heads. The female Pinyon Jay looks quite similar to the male in terms of its appearance.
In terms of diet, Pinyon Jays primarily feed on Pinyon-pine seeds, acorns, various fruits, and grains. However, they are not picky eaters and also consume insects, lizards, snakes, nestling birds, and small mammals.
While they may not be regular visitors to bird feeders, you can attract Pinyon Jays by offering whole peanuts, sunflower seeds, suet, and cracked corn.
Pinyon Jays tend to inhabit forested areas characterized by Pinyon-juniper trees, sagebrush, scrub oak, and other types of pine trees.
When it comes to nesting, Pinyon Jays construct large, bulky nests made of sticks and twigs in trees, often at heights ranging from 3 to 115 feet above the ground. They typically have one brood per breeding season, with each brood containing 2-5 eggs. The eggs are relatively large, measuring between 1.3 to 1.5 inches in length, and they are pale blue with dark brown specks. The incubation period for these eggs lasts for approximately 17 days, and the young birds, or fledglings, typically leave the nest between 21 to 22 days after hatching.
Purple Martin

- Scientific name: Progne subis
- Lifespan: about 5 to 7 years
- Size: 7-inch
- Native to: North America
The Purple Martin is a medium-sized bird, approximately 8.5 inches in length, known for its distinct appearance. It boasts a blue-purple head, back, and belly, along with black wings and tail.
In terms of diet, Purple Martins primarily feed on insects, with a particular fondness for dragonflies.
Although they are not commonly seen at bird feeders, Purple Martins are known to be social birds and are usually found within 100 feet of human dwellings. They often exist in large colonies, where multiple birds live together.
When it comes to nesting, Purple Martins are cavity nesters, meaning they nest in cavities or hollow spaces. They primarily utilize manmade nest boxes designed to accommodate a colony of birds. During the breeding season, they typically have one brood, which consists of 4-5 white eggs. The incubation period for these eggs lasts for approximately 15-18 days, and the young birds, or fledglings, typically leave the nest after 26-30 days.
Purple Martins are migratory birds. They spend their winters in South America and migrate north during the breeding season to raise their young.
Their breeding range includes the Pacific northwest coast of Washington, Oregon, and California, as well as parts of Arizona, Utah, and Colorado. They are also found in the eastern half of the United States and the southern parts of Canada’s Alberta, Manitoba, Saskatchewan, and Ontario. During the winter months, Purple Martins can be found in South America.
Red-breasted Nuthatch

- Scientific name: Sitta canadensis
- Lifespan: 6 years.
- Size: 4.5 in
- Native to: North Americ
The Red-Breasted Nuthatch is a small bird, measuring about 4.5 inches in length. These birds have distinctive features, including grayish-blue backs, a white head adorned with black stripes over each eye, and an orange-cinnamon-colored breast. They also have a pointed, pick-like beak. Female Red-Breasted Nuthatches share a similar appearance, but their undersides tend to have more muted colors. You’ll often spot them climbing upside-down on deciduous trees while foraging for insects beneath the bark.
When it comes to their diet, Red-Breasted Nuthatches primarily feed on insects, spiders, and various other bugs.
While they may not be regular visitors to bird feeders, you can attract Red-Breasted Nuthatches by offering suet, sunflower seeds, shelled peanuts, and fruit as feeder food.
Red-Breasted Nuthatches are commonly found in forested areas, particularly those primarily comprised of coniferous trees like pines. In the eastern regions, you can also find them in wooded areas with deciduous trees. During the winter months, southern populations of these birds tend to prefer mountainous regions before heading to lower-lying areas.
For nesting, Red-Breasted Nuthatches are cavity nesters, and they have a unique habit of excavating their own holes for nesting. During the breeding season, they typically have one brood, and each brood contains about 6 eggs. These eggs are white and speckled with red-brown markings.
Red-Breasted Nuthatches exhibit partial migratory behavior. While many remain in their year-round range throughout the year, others migrate south for the winter. Their year-round range encompasses southern Alaska, the western third of the United States, northern Minnesota and Wisconsin, Michigan, Pennsylvania, New England, and all Canadian provinces except Nunavut. During the winter, you can find them in U.S. states that are not part of their year-round range.
Rock Pigeon

Image Source
- Scientific name: Columba livia
- Lifespan: 6 years
- Size: 11-13 inches
- Native to: Europe North Africa and India, it now lives in wild or semi-wild conditions in cities all over the world, including most of North America
The Rock Pigeon is a large bird, measuring approximately 12-14 inches in length. These birds have a plump appearance, characterized by blue-gray wings with black pointed tips, short red legs, a round and wide black tail, and an iridescent neck.
When it comes to their diet, Rock Pigeons primarily feed on grains, seeds, and fruit. They are often spotted scavenging for food around trash cans in urban areas.
While they may not be regular visitors to bird feeders, you can attract Rock Pigeons by offering foods like millet, cracked corn, black-oil sunflower seeds, safflower, and peanut hearts.
Rock Pigeons are commonly found in areas around cities, towns, and farmlands. They are adaptable birds that thrive in urban environments.
For nesting, Rock Pigeons construct large nests made of sticks and grass. They often choose locations with ledges, such as highway overpasses, barns, bridges, and tall buildings. During the breeding season, they can have multiple broods in a single year, ranging from 1 to 6 broods. Each brood typically contains 1-3 eggs, which are white in color. The incubation period for these eggs lasts for about 18 days, and the young pigeons, or squabs, fledge at around 25-32 days of age.
Rock Pigeons are not migratory birds. They stay within their year-round range throughout all seasons of the year. Their year-round range includes every U.S. state, the southernmost edges of Canada, and Mexico.
Steller’s Jay

- Scientific name: Cyanocitta stelleri
- Lifespan: 16 years
- Size: 12–13 in
- Native to: Western North America and the mountains of Central America
The Steller’s Jay is a large bird, measuring around 11.5 inches in length. These birds are known for their striking appearance with a dark blue body and crest, contrasted by a black head and crest adorned with spots of blue. Female Steller’s Jays share a similar look to the males.
In terms of diet, Steller’s Jays have a varied menu. They primarily feed on nuts, seeds, fruits, and insects. Additionally, they are known to consume other birds’ eggs and nestlings, as well as small animals.
Although they may not be frequent visitors to bird feeders, you can attract Steller’s Jays by offering foods like whole peanuts, sunflower seeds, and suet.
Steller’s Jays are typically found in forested areas that feature a mix of tree types, including coniferous and deciduous trees.
For nesting, Steller’s Jays create large open-cup nests constructed from twigs, bark, and mud. They usually position these nests high up in conifer trees. During the breeding season, they typically have one brood, consisting of 4-5 eggs. These eggs have a distinctive appearance, with blue or green coloration and dark brown, purple, or olive spots. The incubation period for these eggs lasts for approximately 16-18 days, and the young jays, or fledglings, typically leave the nest at around 16-18 days old.
Tree Swallow

Image Source
- Scientific name: Tachycineta bicolor
- Lifespan: 5 years
- Size: 14 cm
- Native to: North America
The Tree Swallow is a small bird, measuring about 5-6 inches in length. These birds have a distinct appearance, featuring dark metallic blue to blue-green feathers with a white belly. They also have notched tails and pointed wingtips. While the males exhibit these vibrant colors, female Tree Swallows share a similar appearance but tend to be a bit duller in coloring.
When it comes to their diet, Tree Swallows primarily feed on insects and small fruits, which they catch while in flight.
Although they are not typically seen at bird feeders, Tree Swallows prefer open areas such as fields, large lawns, and marshes for foraging and nesting.
Speaking of nesting, Tree Swallows are cavity nesters. They often choose to nest in old, dead trees or existing holes left behind by other cavity-nesting birds. During the breeding season, they lay 2-8 eggs. These eggs start with a light pink color and gradually fade to white. The incubation period for these eggs lasts for approximately 14-15 days, and the young Tree Swallows, or fledglings, typically leave the nest at about 18-22 days of age.
Western Bluebird

- Scientific name: Sialia mexicana
- Lifespan: 6 to 10 years
- Size: 5.9 to 7.1 in
- Native to: North American
The Western Bluebird is a small bird, measuring around 7 inches in length. These birds have distinctive appearances, with deep blue underparts and an orange-chestnut back and breast in males. In contrast, females have a gray-blue coloration, light blue wings and tail, and a pale chestnut breast.
In terms of diet, Western Bluebirds primarily feed on insects, fruits, and berries.
While they may not be regular visitors to bird feeders, you can attract Western Bluebirds by offering them mealworms as feeder food.
These birds are typically found in open woodlands, particularly those with pine and oak trees, as well as orchards and farmland that have some trees for perching and nesting.
Speaking of nesting, Western Bluebirds are cavity nesters, meaning they nest in existing holes or cavities. They often utilize old woodpecker holes or manmade nesting boxes. During the breeding season, they can have two broods, with each brood containing 4-5 eggs. These eggs are usually pale blue without blemishes, although they can sometimes be white. The size of these eggs varies, with a length ranging from 0.8 to 2.4 inches and a width of about 0.8 inches. The incubation period for these eggs lasts from 12 to 18 days, and the young Western Bluebirds typically fledge at about 20 days of age.
White-breasted Nuthatch

Image Source
- Scientific name: Sitta carolinensis
- Lifespan: 2-6 years
- Size: 13-15 centimeters (5-6 inches)
- Origin: North America
The White-Breasted Nuthatch is a small bird, typically measuring between 5 to 6 inches in length. These birds have a distinct appearance with a gray-blue back, a white head adorned with a black cap, and a chestnut-colored area under their tail. They also possess a long, thin, pick-like beak. Female White-Breasted Nuthatches share a similar look, except their cap and neck are gray. These nuthatches are often observed climbing upside-down on deciduous trees as they search for insects beneath the tree bark.
When it comes to their diet, White-Breasted Nuthatches primarily feed on insects and seeds.
While they may not be frequent visitors to bird feeders, you can attract White-Breasted Nuthatches by offering suet, sunflower seeds, and shelled peanuts as feeder food.
White-Breasted Nuthatches tend to reside in habitats near mature deciduous and mixed forests, as well as wooded suburban areas such as orchards, parks, and backyards.
For nesting, White-Breasted Nuthatches are cavity nesters. They typically have one brood per breeding season, consisting of 5-9 eggs. These eggs are white with brown markings. The incubation period for these eggs lasts for approximately 11-12 days, and the young nuthatches fledge at about 13-14 days of age.
Unlike migratory birds, White-Breasted Nuthatches do not undertake seasonal migrations. They remain in their year-round range throughout all seasons of the year. However, a small portion of the population may migrate to a strip in the south-central United States for the winter months. Their year-round range includes every U.S. state, Canada’s southern provinces, and Mexico.
Final Thoughts on Blue Birds in Utah
Bluebirds in Utah are not only captivating and charming birds but also important indicators of the health of our local ecosystems. Their presence reminds us of the delicate balance of nature and our role in preserving it. By supporting conservation efforts, providing suitable nesting spaces, and being mindful of our environmental impact, we can help ensure that these beautiful blue birds continue to thrive in Utah.

![9 Species Of Hawks In Ohio [Images + Ids]](https://birdsology.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/4550158342_ef430e7abc_b-600x400.jpg)
![3 Types of Doves in Connecticut [Images + IDs]](https://birdsology.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/51966837857_e62c6fbc37_b-600x400.jpg)
![10 Beautiful Red Birds in Washington [Images + IDs]](https://birdsology.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/47057120154_e3fa046c41_b-600x400.jpg)
![10 Beautiful Red Birds in Maryland [Images + IDs]](https://birdsology.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/14235697222_3abaaf211f_b-600x400.jpg)