Surprisingly, a lot of creatures may resemble beavers, particularly in situations when you’re outdoors and can’t acquire a clear enough picture for a solid identification. Numerous mammal species have evolved to become semi-aquatic due to their adaptation to watery habitats. Maybe you see a brown, fluffy form floating across the water, or you hear a splash. But how can you be certain of the kind of semi-aquatic animal you observed?
We are going to assist you in recognizing seven of the most prevalent beaver impersonations in the wild. We’ll examine these brown-furred creatures’ traits in more detail and find out what distinguishes them from beavers.
Synopsis for Quick Read
Beavers have a scaly tail that resembles a paddle, webbed feet, and a huge, stocky build. In the environments where they are located, there is often evidence of fallen trees and chewed branches. It is most certainly a beaver if the animal has a branch in its jaws.
Look for the tail first when recognizing semi-aquatic creatures in the wild. Is it broad or thin? Is there fur on it? Is it scaled? Secondly, does the fur seem soft or coarse? Does the animal’s body have a more rounded or streamlined appearance? Beavers seem rounded and hefty as they emerge from the water. Even in the water, they seem enormous.
Beaver impersonators:
How Does a Beaver Appear?
Beavers have a robust physique and a coat that ranges in color from very dark brown to almost yellow-brown. These big animals have a weight of more than fifty pounds (22.5 kg)! Their tails are broad, flattened, and have a scaly appearance. Their back feet are webbed. Sometimes, in an attempt to frighten away any predators, they would smack their tails on the water’s surface.
A adult beaver may reach a maximum height or length of 2.5 to 3 feet (75-90 cm).
It is more uncommon to observe one out on land since they are mostly found in the water. Eaters of bark, leaves, buds, and fruits, beavers are strictly herbivores. With their big, powerful, constantly expanding front teeth, they chop down trees, chew off branches, and remove bark.
Actually, there are only two species of beavers worldwide:
The European or Eurasian beaver, or castor fiber, is found in certain regions of Asia and Europe.
Castor canadensis, the North American Beaver, is found in Canada, the United States, and a few regions of South America.
The presence of downed trees is one identifying clue that might help you determine whether the animal you witnessed was a beaver or not. Beavers are present in the region if these trees have a pile of woodchips below them and the recognizable scratch scars of active beaver teeth.
These hardworking creatures design their surroundings by constructing dams and lodges out of branches. They are often thought of as keystone species since they alter the environment around them and become an essential part that the ecosystem as a whole relies on.
Seven Species That Remind Us of Beavers
The animals on our list today are all related by having brown fur and semi-aquatic lifestyles. There is a chance that their ranges and habitats would overlap, therefore signs such as dams may not always indicate the presence of beavers.
1. Muskrat

Scientific Name: Ondatra zibethicus
When it comes to mistaking an animal for a beaver, these creatures resemble beavers among the most likely possibilities. Their semi-aquatic lifestyle and thick brown hair make them an excellent choice to pose as a beaver. The species that most closely resembles a “small beaver-like animal” is this one.
Similar to beavers, muskrats consume plants and are often seen swimming with leaves in their jaws. But unlike beavers that gnaw branches off trees and carry them in the water, muskrats never have real branches in their jaws. Being omnivores, they will also consume frogs, small fish, and shellfish.
Muskrats weigh around 3 to 4 pounds (1.3-1.8 kg) and grow to a maximum length of 20 inches (50 cm), making them smaller than beavers as well. Their tiny, hairless tails resemble those of rats or mice and are far smaller than those of beavers. These “small beavers” resemble rounded furballs when they are on land.
Instead of using branches, they will construct dens out of reeds, cattails, and other plants heaped together.
The round-tailed muskrat is a kind of uncommon muskrat species that, as its name implies, has a more rounded tail than a typical muskrat. However, this species is rare and only found in southern Georgia and Florida.
Do muskrats and beavers coexist?
Indeed, muskrats and beavers consume the same plants and live in similar watery environments including lakes, rivers, and swamps. Thus, it is feasible to come across two species in one location.
2. Coypu Nutria

(Scientific Name: Myocastor coypus.)
The nutria, commonly called a coypu, is another frequently misidentified species as a beaver. They are about half the size of an adult beaver, although sharing the same thick brown fur and semi-aquatic lifestyle. Nutria have the same long, thin, hairless tail as muskrats.
The majority of nutria are found in South America, however some have escaped from the fur trade and established colonies along the Gulf Coast (USA).
It is improbable that they will have nutria-carrying plants in their jaws; instead, they would likely dig for roots and tubers and munch on aquatic grasses. Additionally, they will tunnel underneath instead of making dens or mounds. A nutria may be identified by its distinctly orange incisors.
A mature nutria may weigh up to 25 pounds (16 kg) and measure between 16 and 25 inches (41 and 64 cm) in length. Unlike beaver fur, which appears smooth when wet, the fur may seem gritty.
3. Otter River

(Scientific Name: Lontra canadensis )
The North American river otter is one of the most popular animals that people mistakenly believe has a beaver-like tail due to its hairy tail. Compared to beavers, they have more rounder faces, and they are known to pop their heads out of the water to survey their surroundings while hiding the rest of their bodies underneath the surface.
Otters are carnivores who search for fish in the water quickly, in contrast to beavers. The ponds and regions of slower flow that beavers make beside a river are frequently advantageous to them. Like a beaver’s hind feet, theirs are webbed.
River otters are elegant, thin creatures with very silky hair that, when damp, practically takes on a silvery appearance. Adults may grow to a length of 34–50 inches (0.86–1.27 m) and a weight of around 25 pounds (11.3 kg).
This species may be rather inquisitive about humans and is gregarious and lively. One characteristic that sets them distinct from beavers is that the former prefer to be seen alone and shun people.
4. Mink American

(Scientific Name: Neovison vison)
As severe carnivores, mink differ from most other mammals on our list, which are either herbivorous or omnivorous. They are crafty and ferocious predators that are often seen hunting along riverbanks or the edge of waterbodies for fish and birds, including bird nests where they eat the eggs and chicks.
This creature resembles a weasel in its long, lean physique. When it is still, it sometimes hunches its back. Minks often have fuzzy tails and dark brown fur, with orange-brown highlights sometimes.
Although they are happiest on land, mink are sometimes spotted swimming in the water. However, they seldom swim for long periods of time. Although mink are considerably smaller than otters, they are often confused for them. Adults may range in length from 12 to 18 inches (31 to 45 cm) and weight from 0.4 to 1.6 kg (0.8 to 3.5 pounds).
5. Otter Sea

(Scientific Name: Lontra felina)
You could have seen a sea otter if you have ever encountered a beaver-like animal along the coast between southern California and Alaska. The fur of this animal is the densest of all mammals, with one million hairs per square inch! It needs this heavy insulation since the waters it lives in are chilly.
Sea otters, like their river otter relatives, have webbed paws and a long, fuzzy tail. They may be distinguished from all the other species on our list today by their light brown to cream colored heads.
Often feeding on crabs or crustaceans that they deftly balance on their stomachs as they bob about, they have a distinctive floating motion on their backs.
A beaver is much smaller than this species. Male adults have a maximum length of 4.9 feet (1.5 meters) and a maximum weight of 100 pounds (45 kg)!
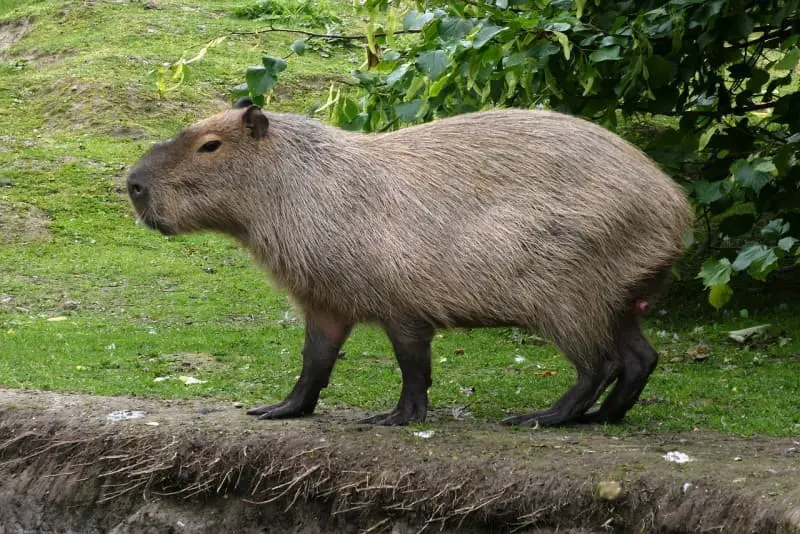
6. The Capybara

Scientific Name: Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris
The capybara may come to mind if you are wondering, “What animal looks like a beaver but without a tail?” At almost two feet (60 cm) tall, this magnificent species is the biggest mouse of all.
Capybaras resemble beavers in appearance, with their stocky, rounded body and somewhat webbed feet. They have brown hair as well, although it tends to be lighter and shaggy rather than sleek.
They live in watery habitats across Central and South America and are skilled swimmers. Like beavers, capybaras are herbivores and eat a similar diet.
The main difference between them and beavers is that they lack a tail, giving them somewhat longer legs and a more terrestrial appearance.
FAQs:
Which animals resemble beavers but lack their tails?
The most frequent offender is the capybara, which resembles a big, long-legged beaver but is tailless. It’s also conceivable that you are seeing a creature that lost its tail in a struggle or an accident, or that the tail was submerged under the water and you were unable to see it.
What larger animal resembles a beaver?
The sea otter and capybara are two of the most prevalent beaver-like creatures that are bigger than beavers. Freshwater habitats are not home to other species that are comparable to them.
What kinds of tiny animals resemble beavers?
Beaver-like smaller mammals include muskrats, nutria, and American mink. Since they are all semi-aquatic, these species will live in habitats similar to those of beavers. Although they are considerably more difficult to see due to their small size and elusive nature, water shrews and water voles may also be found in the same watery habitats. They have long tails and brown fur too, but unlike beavers, which have flat, wide tails, muskrats and nutria have thinner, hairless tails.
What animal resembles both a duck and a beaver?
Most likely, the platypus, often referred to as the duck-billed platypus, is what comes to mind. Another semiaquatic, brown-furred animal that lives in watery habitats. But this species lives far apart from beavers in Australia. However, it also possesses a tail that resembles a beaver’s and webbed feet.


![13 Birds with Big Mouths [Some are Really Scary]](https://birdsology.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/29-600x400.jpg)
![Are Mockingbirds Aggressive To Other Birds? [Explained]](https://birdsology.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/14632.webp-600x400.webp)

