If you’re a bird enthusiast, you might have heard about the variety of doves that inhabit California. From the Common Ground-Dove to the White-winged Dove, these birds are fascinating creatures that are beloved by birdwatchers and nature enthusiasts alike. Doves are known for their gentle cooing and stunning feathers, making them an incredible sight to behold. California, with its diverse landscape and temperate climate, provides the perfect environment for these birds to thrive. In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at the different species of doves that call California home and explore their unique characteristics and behaviors. Whether you’re a seasoned birder or just starting out, there’s something to discover about these beautiful birds.
Types of Doves in California:
There are several species of doves in California, each with its own unique features and traits. Some of the most common ones are:
- Mourning Dove
- Eurasian Collared-Dove
- White-winged Dove
- Band-tailed Dove:
- Rock Pigeon
Mourning Dove
Image Source
- Scientific name: Zenaida macroura
- Lifespan: 2-5 years
- Size: 9-13 inches
- Native to: Southern Canada to central Mexico
The Mourning Dove is the most common species of dove in California. They are named for their distinctive mournful cooing call, which is a familiar sound in many suburban and rural areas. their cooing sound is often heard in the early morning and late evening hours. These birds are about 12 inches long with a wingspan of 17 inches. They have plump, round bodies, small heads, and long, tapered tails. The plumage of mourning doves is generally brownish-gray with black spots on the wings. They also have a distinctive black marks on their face below their eyes.
Mourning doves are primarily seed-eaters, feeding on a variety of seeds from plants such as grasses, weeds, and grains. They are also known to eat insects and snails.
These birds are monogamous and form pairs during the breeding season. They build their nests on tree branches or other elevated surfaces using twigs, grass, and other materials. Females usually lay two eggs, and both parents take turns incubating them for about two weeks. After hatching, the young are fed a special type of milk called “crop milk” that is produced by the parents. The chicks fledge after about two weeks and become fully independent about a week later.
Mourning doves are popular game birds, and many people enjoy watching and feeding them in their backyards. They are also important for seed dispersal and play a role in maintaining the ecosystem.
White-winged Dove
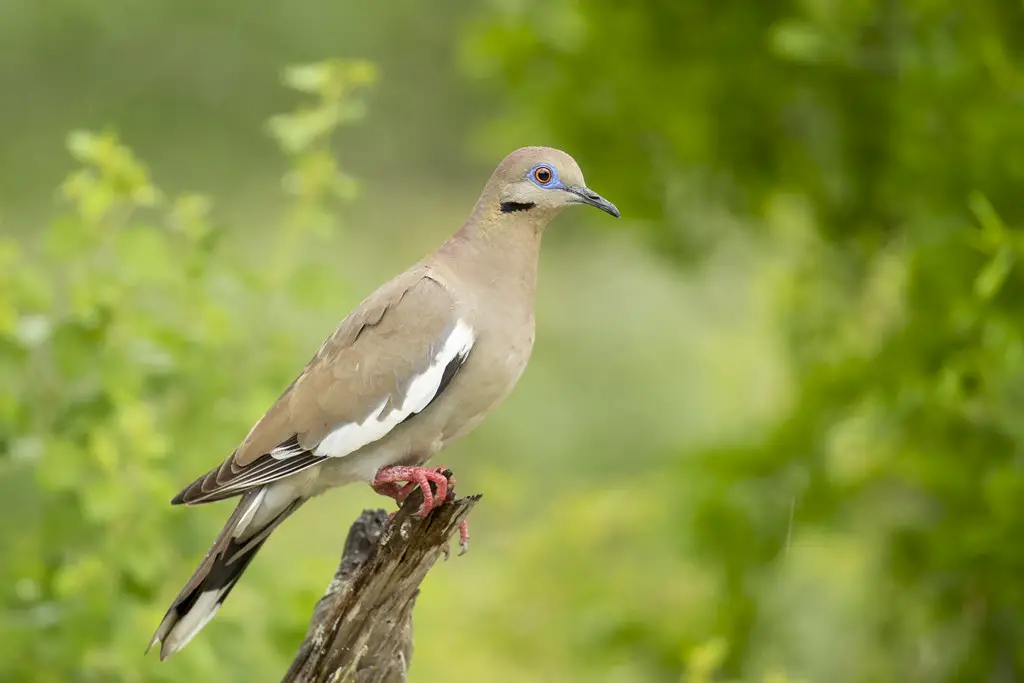

Image Source
- Scientific name: Zenaida asiatica
- Lifespan: 10-15 years
- Size: 11 in
- Native to: Southwestern United States through Mexico, Central America, and the Caribbean
The White-winged Dove is found primarily in the southern parts of California. It is a large dove, measuring about 11 inches long, with a wingspan of approximately 20 inches.
These doves have a unique appearance, with a white patch on their wings that contrasts with their light brown body. They also have a distinctive blue eye ring and a long, pointed tail. Both males and females look similar, but males tend to have a more vibrant plumage during the breeding season.
White-winged Doves are primarily seed eaters, but they also consume fruits, insects, and small snails. They are known to be opportunistic feeders and will eat a wide variety of food depending on what is available.
During the breeding season, these birds form monogamous pairs and build their nests in trees, shrubs, or cacti. Females usually lay two eggs, and both parents take turns incubating them for about two weeks. The chicks fledge after about two weeks and become fully independent about a week later.
White-winged Doves are famous game birds, and their populations are closely monitored by wildlife management agencies. They are also appreciated by birdwatchers for their unique appearance and behavior. In some areas, they are considered a pest because they can cause damage to crops and gardens. Overall, White-winged Doves are an important part of the ecosystem and play a role in seed dispersal and pollination.
Inca dove

Image Source
- Scientific name: Columbina inca
- Lifespan: 8 years
- Size: 6.5–9.1 in
- Native to: Southwestern United States and in northern Central America
The Inca Dove is found primarily in the southwestern parts of California. It is named after the ancient Inca Empire due to its association with similar arid habitats.
These doves are small, measuring about 8 inches long, with a wingspan of approximately 11 inches. They have a distinctive appearance, with a scaly pattern on their wings and a slender, pointed tail. Their plumage is grayish-brown with black and white spots on their wings.
Inca Doves are primarily seed eaters, but they also consume fruits and insects. They are known to be opportunistic feeders and will eat a variety of food depending on what is available.
During the breeding season, these birds form monogamous pairs and build their nests in trees, shrubs, or cacti. Females usually lay two eggs, and both parents take turns incubating them for about two weeks. The chicks fledge after about two weeks and become fully independent about a week later.
Inca Doves are a common sight in many suburban and rural areas, and their cooing call is a familiar sound. They are appreciated by birdwatchers for their unique appearance and behavior. Overall, Inca Doves are an important part of the ecosystem and play a role in seed dispersal and pollination
Band-tailed Dove

The Band-tailed Dove is found in forested areas of California. It is named after the distinctive band on its tail feathers.
These doves are about 13 inches long with a wingspan of approximately 23 inches. They have plump, round bodies, small heads, and long, pointed tails. Their plumage is generally grayish-brown with a lighter-colored head and neck.
Band-tailed Doves are primarily seed eaters, but they also consume fruits, insects, and snails. They are known to be opportunistic feeders and will eat a variety of food depending on what is available.
During the breeding season, these birds form pairs and build their nests in trees or shrubs. Females usually lay one or two eggs, and both parents take turns incubating them for about two weeks. The chicks fledge after about two weeks and become fully independent about a week later.
Band-tailed Doves are an important game bird, and their populations are closely monitored by wildlife management agencies. They are also appreciated by birdwatchers for their unique appearance and behavior. In some areas, they are considered a pest because they can cause damage to crops and gardens. Overall, Band-tailed Doves are an important part of the ecosystem and play a role in seed dispersal and pollination.
Rock Dove:

Image Source
- Scientific name: Columba livia
- Lifespan: 6 years
- Size: 11-13 inches
- Native to: Europe to North Africa and India, it now lives in wild or semi-wild conditions in cities all over the world, including most of North America
The Rock Dove, also known as the pigeon, is a familiar bird found in urban areas throughout California. They are often seen in urban areas and have become well-adapted to living in close proximity to humans.
Rock Doves are medium-sized birds, measuring about 11-15 inches long with a wingspan of approximately 24-28 inches. They have plump, round bodies, small heads, and short, stout legs. Their plumage is typically grayish-blue with iridescent feathers on their necks and wings.
Rock Doves are primarily seed eaters, but they also consume fruits and insects. They are known to be opportunistic feeders and will eat a wide variety of food depending on what is available.
These birds are known for their cooing call, which can be heard throughout urban areas. During the breeding season, they form pairs and build their nests in sheltered areas such as building ledges or under bridges. Females usually lay two eggs, and both parents take turns incubating them for about two weeks. The chicks fledge after about four weeks and become fully independent about a week later.
Rock Doves are often considered a pest in urban areas due to their large populations and tend to roost on buildings, leading to droppings and damage to structures. However, they also have a cultural significance and have been used as messenger birds, homing pigeons, and even pets. Overall, Rock Doves are an important part of the urban ecosystem and play a role in seed dispersal and pollination.
Interesting Facts About Doves in California
- Doves in California are considered a symbol of peace and love and are often used in artwork and literature.
- The mourning dove is the state bird of California and is known for its beautiful cooing sound.
- Doves are also known for their ability to navigate using the earth’s magnetic field.
- Some species of doves in California, such as the white-winged dove, have been known to travel long distances in search of food and water.
Final Thoughts
California is home to several species of doves, including the mourning dove, white-winged dove, and Eurasian collared dove. These birds are an important part of the state’s ecosystem, contributing to seed dispersal and serving as prey for predators such as hawks and falcons. Despite being a popular game bird, mourning doves are also protected under state and federal regulations, highlighting the importance of responsible hunting practices and conservation efforts to ensure their continued survival. As urbanization and habitat loss continue to threaten wildlife populations, it is crucial that we take steps to protect and preserve the habitats that doves and other birds depend on. By promoting conservation efforts and responsible hunting practices, we can help ensure that these beautiful birds continue to thrive in California for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the most common species of dove in California?
The mourning dove is the most common species of dove in California.
What is the distinctive eye ring of doves in California for?
The eye ring of doves in California helps to protect their eyes from the sun.
Are doves in California monogamous?
Yes, doves in California form strong pair bonds with their mates and are monogamous.
Where are the best places to see doves in California?
Doves can be found throughout California, but they are especially common in suburban areas with trees and shrubs, as well as in agricultural areas with crops such as sunflowers and wheat.
Are there any laws or regulations about hunting doves in California?
Yes, California has regulations governing the hunting of doves. The hunting season typically runs from September to December, and hunters must have a valid hunting license and follow specific rules regarding bag limits, shooting hours, and other factors.
How can I attract doves to my yard or garden?
Doves are attracted to areas with a mix of open ground and shrubs or trees for cover. Providing a source of water, such as a bird bath or fountain, can also help attract doves to your yard.
What is the typical lifespan of a dove in California?
The lifespan of a dove in California varies depending on the species and other factors but generally ranges from 2 to 5 years in the wild. In captivity, some species can live up to 15 years.
What do doves eat in California?
Doves in California primarily feed on seeds, including those from grasses and crops such as sunflowers and wheat. They may also eat small insects and other invertebrates.
Are doves considered pests in California?
While doves are not typically considered pests in California, they can sometimes cause damage to crops and gardens. Some people also consider them a nuisance due to their droppings and noise. However, they are protected under California law and cannot be harmed or killed without a permit.


![10 Beautiful Red Birds in Alaska [Images + IDs]](https://birdsology.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/45-10-600x400.jpg)
![13 Beautiful Red Birds in New Mexico [Images + IDs]](https://birdsology.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/45-17-600x400.jpg)
![10 Beautiful Red Birds in South Carolina [Images + IDs]](https://birdsology.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/14235697222_3abaaf211f_b-600x400.jpg)
![10 Species Of Hawks In North Dakota [Images + Ids]](https://birdsology.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/WhatsApp-Image-2023-02-28-at-11.31.52-PM-600x400.jpeg)